Economy
Indian Railway's 2025 milestones to set the stage for 2026
Published On Sun, 28 Dec 2025
Asian Horizan Network
0 Views

New Delhi, Dec 28 (AHN) As many as 42 projects of the Indian Railways, including innovation, indigenisation, track renewals, electrification works, and "airport-like facilities" at redeveloped stations to redefine rail travel, worth over Rs 25,000 crore, were commissioned in 2025 to make passenger and freight trains safer and faster in the country, an official statement said on Sunday.
The New Year is all set to offer comfortable sleeper journeys in long-distance travels through Vande Bharat & Amrit Bharat trains, cutting short the journey time, as well as giving travellers the branded food & beverage options at railway stations, according to a year-end review released by the Ministry of Railways.
During the calendar year 2025, Indian Railways introduced 15 Vande Bharat Express trains. As on December 26, a total of 164 Vande Bharat train services are running across the Indian Railways network. Looking ahead, the upcoming Vande Bharat Sleeper is set to transform overnight travel. It will combine speed, comfort, and modern amenities for long-distance passengers.
Another 13 Amrit Bharat Express trains, which are fully non-AC trains, have also been introduced. A total of 30 Amrit Bharat train services are now running across the Indian Railways network to provide quality services to the common man.
Besides, Namo Bharat Rapid Rail Services are designed for high-frequency and regional connectivity, strengthening short and medium-distance mobility in high-demand corridors.
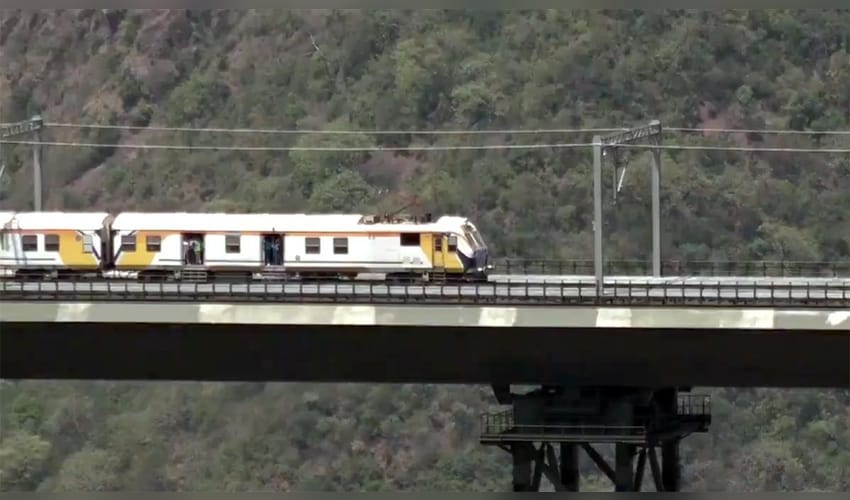
Landmark projects completed during the year include opening the country’s first vertical-lift rail bridge at Pamban, bolstering Kashmir connectivity with all-weather rail links (including the world’s highest Chenab bridge), and extending rail access into the Northeast with the new Bairabi–Sairang line.
Between April 1 and November 30, Indian Railways commissioned over 900 kilometres of new track lines. Besides laying the new tracks, the focus is to renew the existing rail tracks to ensure safer, faster and more comfortable travel. Track renewal works have been carried out across 6,880 track km, rails renewed with new rails, and complete track renewal for 7,051 track km has been done during the year, the statement said.
During the period 2014–25, a total of 34,428 km of new track was laid at an average of 8.57 km/day, which is more than twice the average daily commissioning (4.2 km/day) during the period 2009–14.
These modernisation efforts are complemented by the raising of sectional speeds to improve train operations and passenger convenience. Sectional speed has been increased to 130 kmph over 599 track km, covering parts of the Golden Quadrilateral, Golden Diagonal, and other B routes. Further, speeds of 110 kmph have been achieved over 4,069 track km, combining infrastructure upgrades with advanced track machinery to ensure faster, safer, and more efficient train operations.
Electrification of the railway network has been taken up in mission mode. So far, about 99.2 per cent of the Broad Gauge (BG) network has been electrified. Electrification in the remaining network has been taken up. This achievement is significantly higher than the electrification levels of the UK (39 per cent), Russia (52 per cent) and China (82 per cent). A total of 14 Railway Zones and 25 states/Union Territories have now achieved 100 per cent electrification.
In FY 2025-26 (up to November 2025), more than 4,224 hi-tech LHB coaches were also produced, 18 per cent higher than the corresponding period last year. Between 2014-25, production increased 18-fold compared to 2004-14, ensuring safer, smoother and more comfortable journeys.
Indian Railways has made a major leap in modernisation by manufacturing over 42,600 LHB coaches in the last 11 years. LHB coaches are known for higher safety standards, lower maintenance costs and superior operational efficiency.
The Railways have also achieved remarkable progress in safety performance. Consequential Train Accidents during the period 2004-14 was 1711 (average 171 per annum), which has declined to 31 in 2024-25 and further to 11 in 2025-26 (up to November 2025). The safety budget has nearly tripled, rising from Rs 39,463 crore in FY 2013-14 to Rs 1,16,470 crore in the current financial year. Fog safety devices increased from 90 in 2014 to 25,939 in 2025. In the last four months alone, Centralised Electronic Interlocking and Track Circuiting have been completed at 21 stations, the statement said.
Kavach Version 4.0, the latest indigenously developed Automatic Train Protection (ATP) system, has also been commissioned over 738 route kilometres. The safety system assists the Loco Pilot in operating trains within prescribed speed limits by automatically applying brakes in case of human failure and also enables safe train operations during adverse and inclement weather conditions.
Meanwhile, the 508 km Mumbai-Ahmedabad High Speed Rail (MAHSR) Project has achieved physical progress of 55.63 per cent as on November 30, while overall financial progress has touched 69.62 per cent with an expenditure of Rs 85,801 crore, the statement added.